

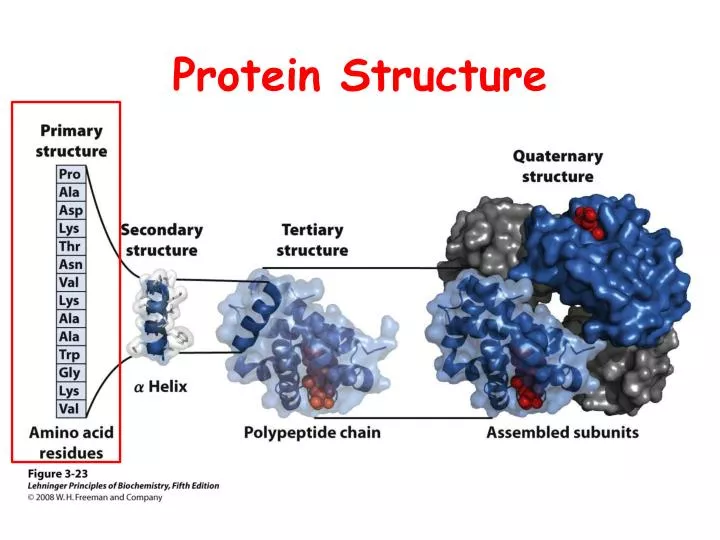
They can be disrupted by the presence of other charged molecules near them. Electrostatic bonds – form between positive and negative charge.Hydrostatic bonds – form between the hydroxyl (OH) group and an adjacent hydrogen molecule, providing a strong bond between polar R groups.The type of bonds involved in the formation of the tertiary protein structure include hydrogen bonds, electrostatic or ionic bonds, covalent bonds or hydrophobic bonds. The tertiary structure can therefore be deranged if there is disruption to the bonds between R groups, causing the structure to lose its shape and resulting in a loss of function. Folding of the polypeptide chain occurs via an i nteraction between the R groups of amino acids. This tends to be globular in shape and contains a binding site for the protein action. Tertiary protein structure is the folding of the polypeptide chain into a unique 3D structure. The sheets can be in parallel or antiparallel.īy Thomas Shafee, via Wikimedia Commonsįigure 3 – Structure of an alpha helix and beta-pleated sheet Tertiary Protein Structure Beta-pleated sheet – formed by hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl group of one amino acid on one sheet and the hydrogen molecule of an amino acid on another sheet.The strong bonds and stability of this structure give it a strong tensile strength, which allows it to form the shape seen in DNA. Alpha-helix – a coil formed by hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl group and the amino group of different amino acids.Secondary protein structure is the repetitive folding of polypeptide chains by hydrogen bonds between the hydroxyl (OH) group and the hydrogen molecule of the adjacent amino acid, leading to the unique shape of the protein. The most common examples are the alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheets. These bonds form between the N terminal and C terminal of amino acids and are highly resistant to heat or chemicals.Īny mutation in this amino acid sequence can affect protein folding, leading to problems with the protein’s function. Primary protein structure is when amino acids bound are together via covalent peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. By Kep17, via Wikimedia Commonsįigure 2 – Overview of protein structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
